1. macOS结构
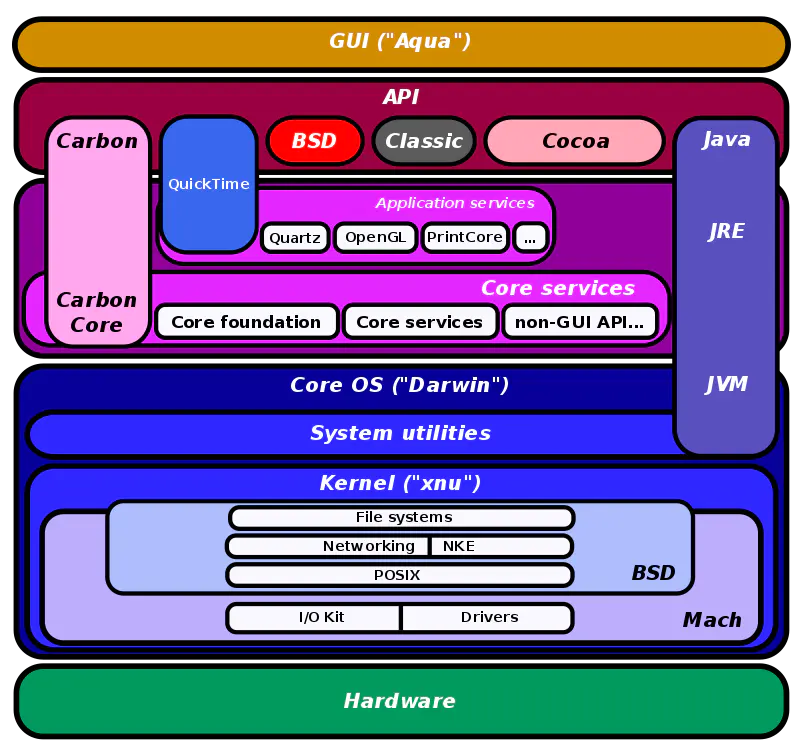
Mac OS X 包含两个主要部分:以 FreeBSD 源代码 和 Mach 微核心为基础的 XUN 混合内核,并在 XNU 上构建的 Darwin 核心系统;及一个由苹果开发,称为 Aqua 的闭源、独占版权的图形用户界面。细分的看,Mac OS X 系统可以分成五层结构,每一层有其代表性技术。
JS是单线程,不能block它,也不适合做CPU密集型工作。如果有可能尽量使用native模块或多线程技术负担JS线程工作。
资源限制内部机制使用的是cgroup类型
目录: /sys/fs/cgroup/systemd
k8s采用request和limit两种限制类型来对资源进行分配
request(资源需求):即运行pod的节点必须满足运行pod的最基本需求才能运行pod。
limit(资源限制):即运行pod期间,可能内存使用量会增加,那最多能使用多少内存,这就是资源限额。
资源类型:
CPU的单位是核心数,内存的单位是字节。
一个容器申请0.5各CPU,就相当于申请1个CPU的一半,可以加个后缀m表示千分之一的概念。比如说100m的CPU,100豪的CPU和0.1个CPU都是一样的。
内存单位:
K,M,G,T,P,E #通常是以1000为换算标准的。
Ki,Mi,Gi,Ti,Pi,Ei #通常是以1024为换算标准的。
Heap 分为young generation, old generation.
Usually, ~20% of the Young Generation survives into the Old Generation. Collection in the Old Space will only commence once it is getting exhausted. To do so the V8 engine uses two different collection algorithms:
node GC时会stop the world,代表主线程被暂停了。
Redux createStore三个主要的属性和方法是{store, getState, dispatch}。createStore是创建一个Redux Store, store是这个Redux Store的引用,getState是返回全局的State, dispatch是发送一个Action. 这个全局State对于JS来说是plain object,每次dispatch都会创建一个新的object,而redux-immutable会使用原来的Immutale Map引用。
其它一些辅助方法:
combineReducers(reducers), 这个是把reducersMap变成一个大reducer object.它接受一个Action和当前State, 然后遍历所有的reducer(这里可能会有性能问题,试想一千个reducer,会影响性能)。
Action是一个Object,它包含type, payload(自定义的负荷). ActionTypes.INIT, 是Redux自带的Action,它的type其实是一个随机生成的字符串。我们不该针对这个ActionTypes.INIT写任何的reducer。
1 | const ActionTypes = { |
1 | return function combination( |
Redux中函数默认值的使用很广泛,第一重要的就是reducers中函数默认值defaultState的使用,然后是createStore中initialState的使用。createStore中初始化Reduxt的Gloabal State就是用到了上面两个函数默认值。
The current React Native Bridge architecture between Native and JS works asynchronously and transfer data in JSON only.
It produces next issues:
Async calls
Many threads and jumps across them: JS, Shadow, Main, Native…
JS and Main threads do not directly communicate (slow UI rendering)
JSON
No data sharing between JS and Native threads
Slow data transfer because of JSON serialisation (bottleneck)
You can make the bridge to any native code Java/Konlin, ObjC/Swift, C++ etc. but you always have the problems from above.
React Native JSI provides API to JS Runtime engine and allows to expose native functions and objects to JS directly - no bridge at all.
It provides next advantages:
Sync call from JS thread to Native and vice-versa
Fast rendering using direct call to UI Main thread
Data sharing between threads
You have to use C++ only to work with JSI because JS Runtime has C++ API but it is possible to make C++ layer between JSI and your existed Java or Swift code.
JSI is foundation for future new React Native architecture which includes: Fabric, TurboModules, CodeGen. Read more: https://github.com/react-native-community/discussions-and-proposals/issues/91
Share
reference:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/69501535/whats-the-difference-between-bridging-a-module-with-c-or-with-jsi-in-react-na